LECTURE SIXTEEN
THE BEHAVIOR OF LAW
NATURE of LAW
- Ubiquitous
- Continuity
- Grounded criteria
- Layered
- Demands deference retrospectively or prospectively
POLICING YOUTH
- Policing: A General Overview
- nature of Policing: roles, functions
- policing is relational: in concert with other hegemonic reproductions of discipline.
- effective policing consists of intelligence gathering practices
- Peel: “Police are the public, the public are the police”
- legal licence and capability: independent crown officers enjoying “original delegated authority”.
These gatekeepers of the criminal justice system enjoy a legal and legitimate monopoly over physical force.
Police Discretion
- interpersonal/ interactional, institutional or organizational, and structural or systemic factors affecting police decisions
- Who benefits from police discretionary practices?
- Independence vs Accountability: continuum/ spectrum
- Role of peace, privacy, private property: reactive policing
- Policing is a persuasive practice has become an apparatus of social control and a mechanism of moral regulation established within the "carceral network" (Foucault, 1977). As Foucault suggests:
- “Disciplinary power is exercised through its invisibility; at the same time it imposes upon those whom it subjects a principle of visibility. In discipline, it is the subjects who have to be seen. Their visibility assures the hold of the power that is exercised over them. It is the fact of being constantly seen, that maintains the disciplined individual in his subjection “(Foucault, 1977: 187)
POLICING RACIALIZED YOUTH
- Policing racialized youths = policing of the poor and unemployed
- All too often, police are perceived by visible and ethnic communities as being aloof from those they serve (Hill, 1985:4).
"to harass and oppress (Head, 1976:1-7) as the new slogan for "to serve and protect"
- police surveillance.
Stephen Lewis, author of the race relations report after the 1992 disturbances in Toronto, met with groups of young people, most of them from visible minority communities.
He states: "Time and time again I was told of the disproportionate numbers of minority youth in detention centres, of the abuse gratuitously heaped upon them, of the woeful lack of 'rehabilitation' opportunities" (Department of Justice, 1993b:4).
As James Baldwin admonished:
"Some of us, white and black, know how great a price has already been to bring into existence a new consciousness, a new people, an unprecedented nation. If we know and do nothing, we are worse that the murderers hired in our name" (Davis et al., 1971:23).
Commissions of Inquiry: the Lewis Report
Underlying conditions
The “war on crime”
Race has always been too easily exploited by the state and its private interests in criminalizing colour thereby obfuscating prevailing racist ideologies in the treatment of crime in Canada, UK and the USA
The policing of youth is qualitatively different from the criminalization of adults especially since the former’s formal social control reflects historical preferences that link explicitly youth to projects of moral regulation
For the police the concept of youth has taken an exaggerated social significance.
- a morality play
- policing strategies - vehicle checks, “stop and frisk”, “carding”
- puffed up charges, “fishing” expeditions, TAVIS,
- Helen Betty Osborne
Police-Racial Minority Youth Encounters
- routine encounters
- In general, it was discovered that youths felt that they were expected to accommodate to the arbitrariness of this authority
- demeanour and deference: competing cultures of cynicism
- provoked frustrations – gestures, appearances, aggression,
- In examining the extent to which racism plays a significant role in the social control of young offenders, a number of questions are proposed. How does the dominant order script police-racial minority youth relations?
- "hands up --don't shoot"
“social class” and good behaviour doesn’t protect (Wortley and Tanner 2003)
A sample list of lost lives
Michael Brown 18yrs
Tamir Rice 12 yrs
Cameron Tillman, a 14yrs
VonDerrit Myers 18yrs
Laquan McDonald 17 yrs
Lawson, Michael Wade (17)
Faraz Suleman (16)
Engdahl, Josh (16)
Matthew Dumas (18) —
“Correcting” Youth
Findings: Barriers
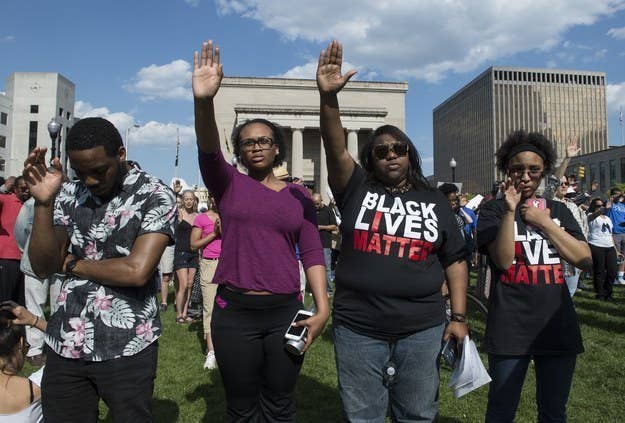
https://www.buzzfeed.com/laurenstrapagiel/canada-is-no-better-on-police-violence-against-black-people?utm_term=.pj5d7B8Ey#.agy4X6E1k

https://www.denverite.com/more-native-american-youth-attend-2016-sand-creek-massacre-memorial-run-23690/

htp://icnacsj.org/2015/02/why-we-need-to-talk-about-the-chapel-hill-shooting/
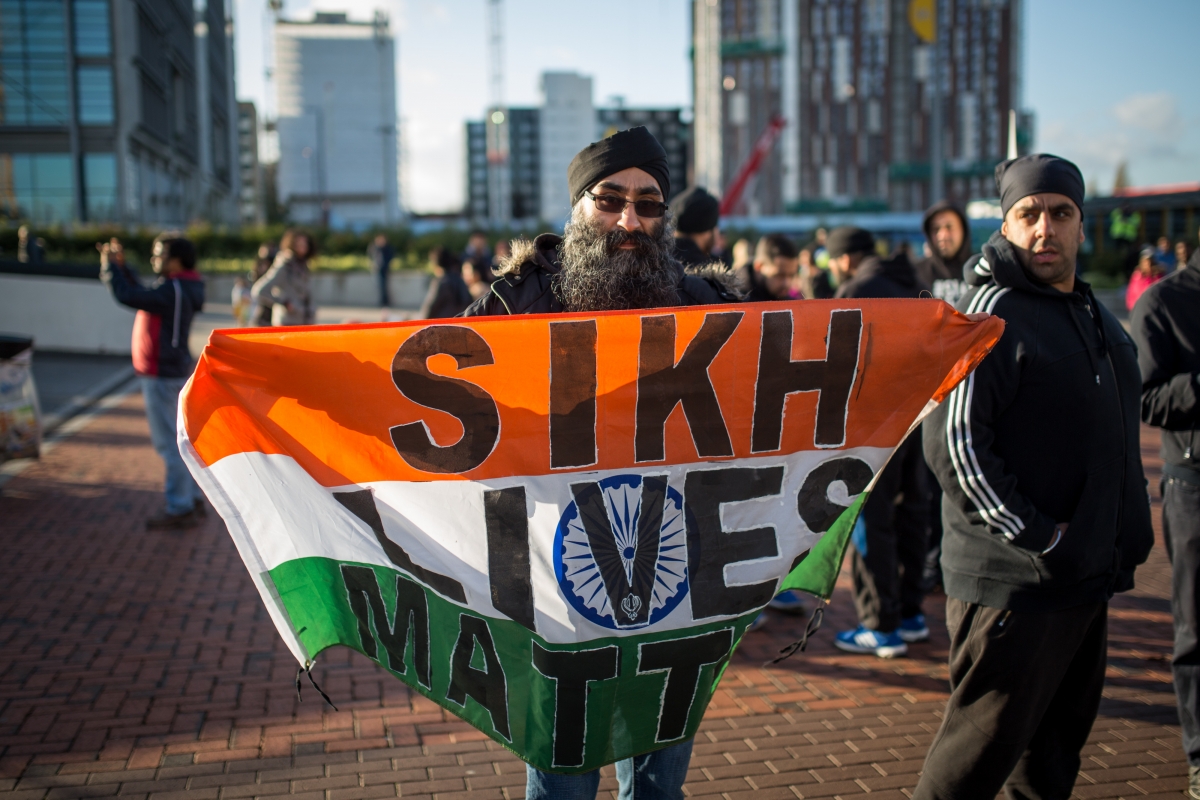

http://www.ibtimes.co.uk/britains-police-force-needs-get-serious-about-logging-islamophobic-attacks-against-sikhs-1532611

https://www.vanityfair.com/news/2016/07/black-lives-matter-all-lives-matter